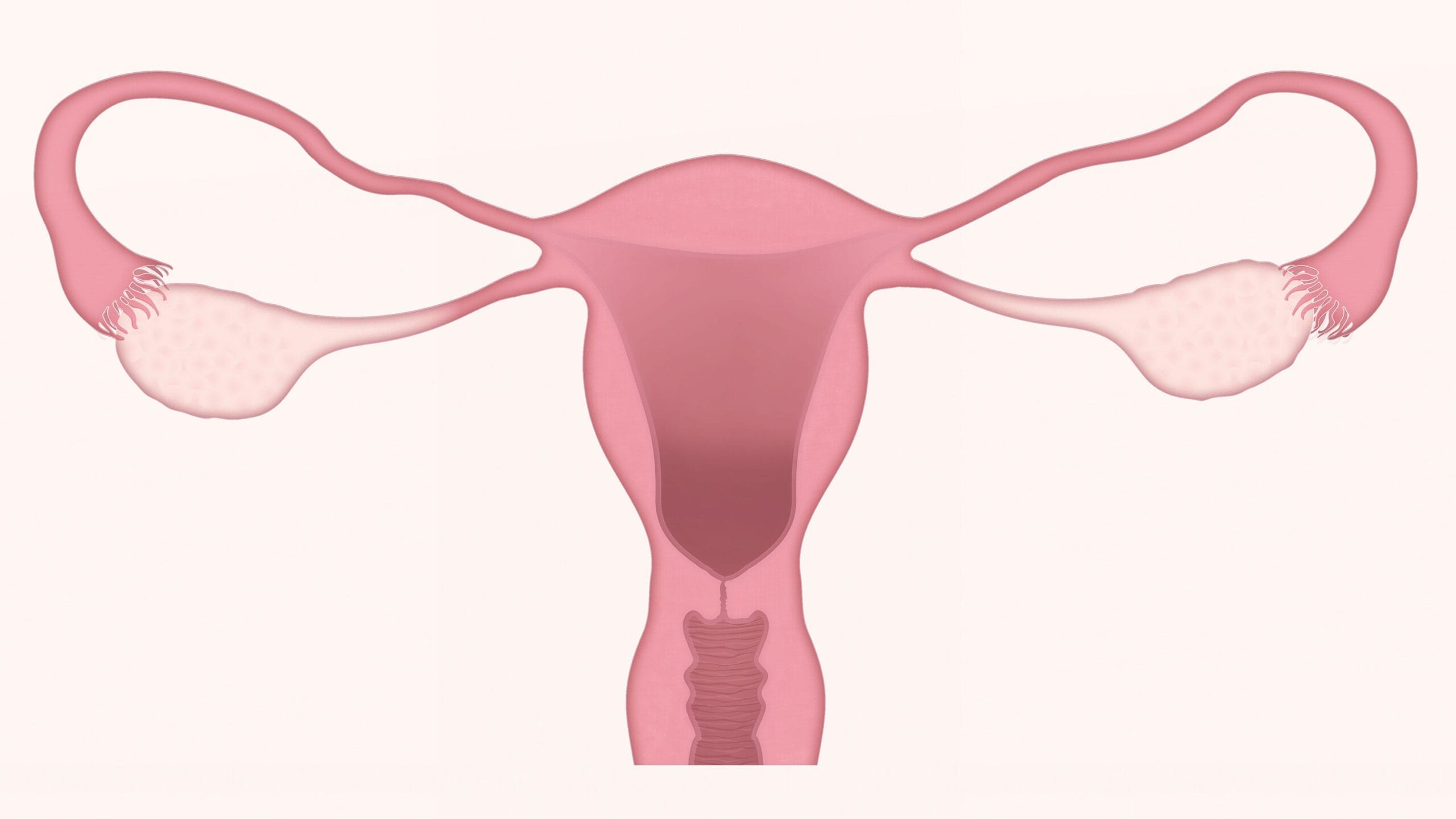
Two female reproductive glands that contain ova, or eggs, are the ovaries. They make the female hormones estrogen and progesterone. In the United States, about 21,750 women will receive a diagnosis of ovarian cancer in 2020. And about 14,000 women will die from it. So, let’s dive in to learn more.
What is ovarian cancer?
Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that starts in the ovary. In general two ovaries are found on each side of the uterus in the female reproductive system. Also, these ovaries, which are about the size of an almond, produce eggs (ova). They also produce the hormones estrogen and progesterone.
Ovarian cancer sometimes remains undetected until it spreads throughout the pelvis and abdomen. Although this cancer is more difficult to treat at this late stage. But early-stage ovarian cancer, in which the disease is confined to the ovaries, is more likely to be treated effectively.
What are the early symptoms of ovarian cancer?
Due to negligible symptoms prevalence, people easily overlook the early symptoms of ovarian cancer. It is because they are similar to other common illnesses or usually come and go.
Early symptoms include the following:
- Abdominal swelling, pressure, and pain
- An anomaly of fullness after eating
- Difficulty eating
- Improved urination
- An increased need to urinate;
Ovarian cancer may also cause other symptoms, including:
- Fatigue
- Indigestion
- Heartburn
- Constipation
- Back pain
- Menstrual irregularities
- Painful intercourse
- Dermatomyositis (a rare inflammatory condition that can cause a skin rash, muscle weakness, and swollen muscles)
Although these symptoms may arise for several different reasons. Hence they cannot only be due to ovarian cancer. At one time or another, many women have any of these problems.
These types of symptoms are mostly temporary and react in most cases to simple treatments.
Causes and risk factors
It arises when cells in this region of the body divide and spread in an uncontrolled way.
It is not known whether ovarian cancer is occurring, although researchers have identified some risk factors.
They shall include:
Family history: Also, having a close relative with a history of ovarian or breast cancer raises a person’s chance of developing ovarian cancer.
Age: Without a doubt, nearly 50% of cases of ovarian cancer occur after 63 years of age.
Breast cancer: Because people with a history of breast cancer tend to have a higher chance of developing ovarian cancer. This may be due to changes in the BRCA gene.
Hormone therapy: Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) during menopause appears to increase ovarian cancer risk.
Obesity and overweight: Ovarian cancer is more prevalent in people with a body mass index (BMI) of more than 30.
Gynecological surgery: Surgery to remove the uterus, called a hysterectomy, can reduce the risk of ovarian cancer by one-third.
Other possible risk factors
Some causes that can raise the risk of some types of ovarian cancer include:
- Having a high level of androgens or male hormones
- Health Factors
- Usage of talcum powder;
However, researchers have not yet found a link between these factors and ovarian cancer.
Types of ovarian cancer
The ovaries consist of three types of cells. Each cell can grow into a different form of tumor:
- Epithelial tumors develop in the tissue layer on the outside of the ovary. About 90% of ovarian cancers are epithelial tumors.
- In the hormone-producing cells, stromal tumors develop. Seven percent of ovary cancers are stromal tumors.
- Germ cell tumors develop in egg-producing cells. Germ cell tumors are rare.
Diagnosis
If a regular screening or symptoms indicate that a person may have ovarian cancer.
Then a doctor may usually do the following:
- Ask a person about their personal and family medical history;
- Perform a pelvic test
Also, they may recommend the following:
- Blood tests: These tests will verify the high level of the marker named CA-125.
- Imaging test: Examples include transvaginal ultrasound, an MRI scan, or a CT scan.
- Laparoscopy: A healthcare provider inserts a thin tube with a camera attached to a small hole in the abdomen. Then sees the ovaries and can take a tissue sample for a biopsy.
- Biopsy: Which requires a microscopic examination of a sample of tissue.
Only a biopsy will prove that a person has cancer. A health care provider can perform this as part of the initial assessment or after surgery to remove a tumor.
Treatment
Treatment will depend on a number of factors, including:
- The type, stage, and level of cancer;
- Age of the individual and general health
- Their personal preferences;
- Accessibility and availability of treatment;
Options appear to involve the following:
Surgery: The decision will depend on the type of cancer and the level to which it has spread. Surgical options include hysterectomy, removal of one or both ovaries, and removal of infected lymph nodes. Nevertheless, the doctor will discuss the best options with the individual.
Chemotherapy: As the purpose of these drugs is to destroy cancer cells. So, if a person is taking chemotherapy drugs by mouth or as an injection or infusion, they will affect the whole body. Intraperitoneal chemotherapy is another option. In this case, the tube delivers the drug directly to the cancer-affected body area. Chemotherapy can have widespread adverse effects, especially if it affects the body as a whole.
Targeted therapy: Some treatments target particular cells that help to promote cancer development. Examples include monoclonal antibody therapy and angiogenesis inhibitors. Targeted treatment aims to reduce adverse reactions by targeting respective functions.
Radiation therapy: This procedure uses x-rays to destroy cancer cells. One way to achieve this is to introduce a radioactive liquid into the peritoneum. This will help people with advanced ovarian cancer.
Immunotherapy (biotherapy): It is aimed to enhance the immune system’s ability to protect the body from disease. Vaccine treatment involves the injection of drugs that can diagnose and destroy a tumor. It will help people with advanced ovarian cancer.
Some of these are relatively recent types of treatment. Some people may opt to enter the clinical trial, which may offer access to some of the newest approaches.
Can ovarian cancer be prevented?
As a matter of fact, there are no proven ways to eliminate the chances of developing ovarian cancer completely. There are, however, measures you may take to reduce the risk.
Factors that have been shown to reduce your risk of developing ovarian cancer include:
- Take oral birth control pills
- Breast-feeding
- Pregnancy
- Surgical operations on the reproductive organs (e.g., tubal ligation or hysterectomy)
The Bottom Line
All forms of ovarian cancer can be treated if a person is diagnosed at an early stage. In later stages, some forms are also highly treatable.
When considering survival statistics for ovarian cancer, it is also worth remembering that medical advances have improved ovarian cancer outlook over the last 20 years.
However, attending a regular screening and finding help if any signs appear will also lead to early diagnosis. It can increase the chance of getting effective treatment.