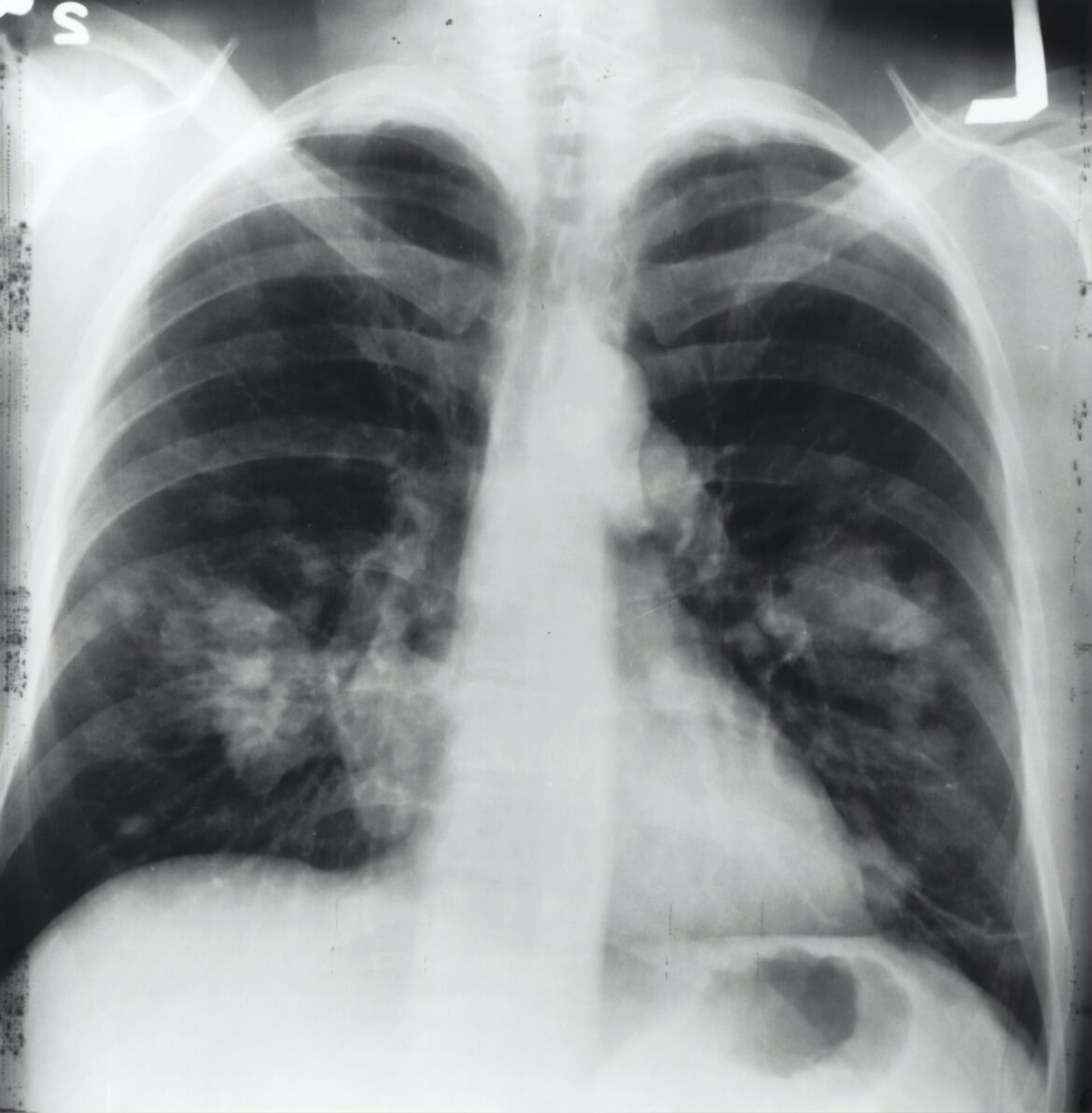
Lung cancer is a growing problem in the United States, and lung cancer is the leading cause of death from cancer. It is one of the most common cancer and has a high death rate. It’s estimated that 1 in 5 Americans will get lung cancer at some point in their lives.
In addition to smoking, other risk factors for developing lung cancer include exposure to environmental tobacco smoke (ETS), occupational exposures, carcinogenic chemicals like radon gas, asbestos, silica dust, air pollution, and genetic predisposition. Let’s discuss each factor in detail:
Smoking
Smoking cigarettes is the biggest risk factor and cause of lung cancer today. This is because smoking puts the body in various chemicals, toxins, and pollutants that can bring about cancer symptoms.
The more a person smokes over the years, the greater the risk of lung cancer and other types of cancer associated with smoking. The longer a person smokes or who are heavy smokers, the more likely they will develop lung cancer.
Smoking exposes the body to carcinogens, also known as cancer-causing agents. These chemicals can cause damage to cells in the lungs and other parts of the body. As the damage develops, the cells are more likely to turn cancerous.
Tobacco
Tobacco is the main ingredient used in making cigarettes. It contains nicotine which is addictive and can lead to dependence on tobacco products. Nicotine causes changes in brain chemistry that affect moods and behaviors. When people stop using tobacco, these effects go away. However, if you continue to use tobacco after quitting, your chances of getting lung cancer increase.
Secondhand Smoke
Secondhand smoke, or passive smoke, may also lead to lung cancer. This occurs when a person does not smoke cigarettes directly but is in the constant presence of someone who does. Secondhand smoke It will help prevent you from breathing in pollutants.
This mainly impacts bartenders, servers, and cigarette shop workers who are around smoking daily. In addition, parents who smoke around their children may put their kids in danger of developing lung cancer over time. There is an increased risk of lung cancer in families with a history of the disease.
Radon
The second most common cause of lung cancer is radon, followed by cigarette smoking. Radon itself is a radioactive gas that releases through the decay of uranium. This is usually found in soil and rocks. Radon is clear, tasteless, and odorless, so it is hard to detect its presence when you are just walking around. This gas seeps through the ground and releases itself into the air, allowing the body to become exposed to it. Too much exposure can lead to lung cancer over time.
Most people do not have problems with radon in the air because of how well it diffuses, but there are times when radon cannot escape into the air thoroughly.
Cancer from radon exposure happens when radon damages the cells that line the lung. Radon can decay quickly, and during that decaying, it releases harmful and radioactive particles into the air.
A person passing through an area with a high concentration of these particles may inhale them. The particles will then pass through the respiratory system to the lungs, where they can damage lung cells and ultimately cause cancer. Cancer from radon usually happens after long-term radon exposure.
Asbestos
Asbestos is a carcinogen, which is a chemical that is known to cause cancer. Mesothelioma, which is rarer than lung cancer, results from asbestos exposure. As a whole, this group of minerals can cause great difficulty when it comes to breathing and the overall function of the respiratory system.
The amount of asbestos that a person gets exposure to can influence their chances of developing an asbestos-related disease, like lung cancer. The amount of time the person was exposed to it may also affect it. Furthermore, the size and general makeup of the asbestos can cause a person to be more at risk for lung cancer. It all depends on the situation.
Individuals who smoke are even more likely to develop lung cancer after asbestos. That is because smoking is the leading cause of lung cancer globally. Therefore, the less exposure a person can have to asbestos and cigarette smoke, the healthier they will be.
Arsenic
Arsenic is one of the toxic substances, and it can be harmful to the environment in high quantities. The International Agency for Research on Cancer has deemed arsenic a group 1 carcinogen. And many of the compounds made of arsenic are also known carcinogens. So these are cancer-causing chemicals that should be avoided if possible.
People who work in glass production, electronic semiconductor manufacturing, and wood preservation are more at risk of arsenic exposure than others, but anyone can find this in their drinking water. Ideally, consumers should consider getting a filtration system for the home to get rid of arsenic in the water, or they should purchase bottled water that has gone through heavy filtration.
Arsenic can get into the lungs and cause damage to lung cells. This can lead to abnormalities in the cells, which can create the appearance of cancer. Smokers are more at risk of this than non-smokers because cigarettes also damage lung cells.
Chromium
Chromium exposure can lead to lung cancer as hexavalent chromium is a human carcinogen. As a person inhales chromium, it can travel to the lungs and cause damage to the cells within. Cancer is simply an abnormality in cells, and the damage caused by chromium could lead to such an abnormality.
Some recent studies have also shown that chromium present in drinking water may cause lung cancer. The more a person has workplace exposures of chromium, the more likely they will develop lung cancer or a similar disease. The duration of the exposure and the amount of chromium present will also play into a person’s risks.
Chromate exposure increases lung cancer risk in smokers, but smoking is still the leading cause of lung cancer.
Nickel
Nickel is a human carcinogen, as determined by the International Agency for Research on Cancer. Much of the research behind nickel, in general, was sparked by a group of nickel refinery workers in Norway who were tested for cancer developing risks per their exposure to nickel.
Water-soluble nickel is more harmful than air-borne nickel, making water soluble nickel more of a cause for cancer than other forms of nickel.
Smokers in this study were more at risk of developing lung cancer than non-smokers, which follows the concept that smoking is the leading cause of cancer in the modern world. It may not expose the body to chromium, but it does create exposure to many other carcinogens that people should stay away from.
Hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons are organic materials that are mainly made up of carbon and hydrogen. They are present in various everyday items, like mineral spirits, gasoline, motor oil, kerosene, rubber cement, solvents, dry cleaning chemicals, paints, and others. Many hydrocarbons come from wood or petroleum-based products, and they can be present in gaseous, liquid, or waxy states.
Overexposure to certain hydrocarbons can lead to the development of lung cancer in the body, although other carcinogens are more likely to spark lung cancer than hydrocarbons.
Most of the hydrocarbons released into the air come from cars, trucks, boats, buses, and other vehicles that have fumes coming from them due to the burning of fossil fuels. This creates pollution that humans can quickly inhale. This pollution may also be caused when paints, cleaning chemicals, solvents, and similar substances are released.
People who smoke have a greater chance of developing cancer since cigarettes have already damaged their lungs. Inhaling hydrocarbons only adds to the problem and can cause cancer development more than it would have been otherwise.
Ethers
As the spread of lung cancer occurred worldwide, scientists began seeking out possible causes for this dreaded disease. In light of that, they went on an investigation to determine if chloromethyl ethers are possible causes of cancer, and their results were pretty conclusive. The scientists conducted a study of workers in the US and the UK. Some were exposed to CMEs throughout their careers, and others were not. The study lasted for thirty years, and it followed the lives and health conditions of these men to determine the connection between ethers and lung cancer.
At the end of the thirty-year study, the researchers found that 25 of 67 deaths from the group were caused by lung cancer, believing that lung cancer can be derived from overexposure to ethers. Most people experienced this exposure in their places of work.
Workers who are smoking on top of getting expose to others were more likely to develop lung cancer. As compared to other because of the carcinogens found in cigarettes. Those who did not smoke decreased their risks dramatically.
Air Pollution
Air pollution can contain a variety of harmful chemicals to the body. Many of these chemicals are carcinogens, which are cancer-causing chemicals. Hydrocarbons and cigarette smoke are some of the more common components of pollution, but there are many potentially harmful toxins in pollution.
As air pollution is inhaled and dispersed into the lungs. The lungs tend to be the organ most affected by pollution exposure. As a result, lung cancer is a potential side effect of living with air pollution. Unfortunately, it is something that many people do not even think about until they have already experienced symptoms of lung cancer.
BOTTOM LINE
Exposure to cigarettes or other carcinogens to increase a person’s risk of developing cancer. Those with a family history of lung cancer or previous lung cancer should avoid heavy pollution exposure. Wearing a mask on the face could reduce exposure levels drastically. For those who smoke, the best way to prevent lung cancer is to reduce smoking and prevent others from inhaling passive smokes.